Wireless (Unguided) Transmission Media :
- A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location .
- A wave is a transfer of energy , usually through a form of matter called a medium .
- There are special type of wave that can travel without a medium , called electromagnetic waves ( Also called WEM waves) , which are waves like radio waves and microwaves.
- The electromagnetic spectrum describes a wide range of different electromagnetic waves .
A little part of electromagnetic spectrum can be used for wireless transmission .
1- Radio Waves Transmission
- Radio waves are EM waves that have wavelengths between 1 millimeter and 100 kilometers ( 0r 300GHZ and 3KHZ in frequency).
- Radio frequency is easy to generate because its has large wavelength and can travel long distance.
- Radio waves are generated by radio transmission and received by radio receivers.
- Radio stations transmit radio waves using transmitters , which are received by the receiver installed in our devices .Both transmitters and receivers use antenna .
- It can penetrate walls easily , so these waves are widely used for communication both indoors and outdoors .
- Radio waves are omnidirectional means they travel in all the directions from the source.
- When an antenna transmits radio waves , they are propagated in all directions.
- A sending antenna send waves that can be received by any receiving antenna . The omnidirectional property has disadvantage too . The radio waves transmitted by one antenna are susceptible to interference by another antenna that may send signal using the same frequency or band.
- It is used Mobile , AM/FM radio , television.
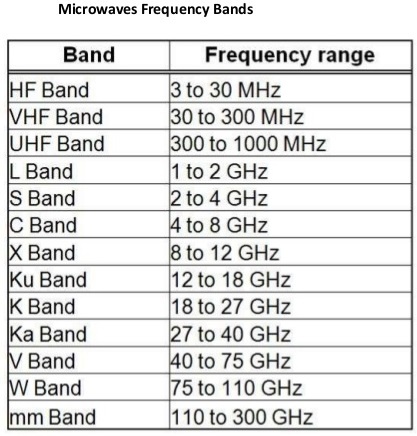
2- Microwaves Transmission :
- Microwaves are a type waves with high frequencies . It can be classified as a subclass of radio waves . The frequency of microwaves lies in the 300MHZ to 300GHZ.
- Unlike radio waves , microwaves are unidirectional , in which the sending and receiving antennas need to be aligned.
- Microwaves are widely used for point - to - point communications because their small wavelength , which means that the signal is focused in to a narrow beam . Additionally , each antenna must be within line of sight of the next antenna.
- Microwaves have higher frequencies and do not penetrate wall like obstacles.
- It is used for satellite communication , navigation , radar , remote sensing and other short distance communication systems .
3- Infrared Waves Transmission :
- Infrared signals have frequencies between 300GHZ to 400GHZ . They are used for short range communication.
- Infrared waves are used for very short distance communication like TV remote , wireless speakers , automatic doors , hand held devices etc.
- Infrared waves having high frequencies prevents interference b/w one system to another.
- Infrared signals have high frequencies and cannot penetrate walls . Due to its short range communication system , the use of an infrared communication system in one room will not be affected by the use of another system in the next room . This is why using an infrared TV remote control in our home will not interfere with the use of our neighbor's infrared TV remote control.
The disadvantages of using Infrared
Infrared signals cannot be used for long distance communication . In addition , we cannot use infrared waves outside a building because sun's rays contain infrared waves that can interfere with communication