What is Microwave ?
- Microwave ( MW ) are a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from 1m to 1mm
- Frequencies between 300MHZ to 300GHZ
Microwave Transmission :
- Microwave transmission is the transmission of information ( Voice , data , television or radio signals ) by microwave radio waves.
- Microwaves are widely used for PPP ( Point - to -Point ) communications because their small wavelength allows conveniently sized antennas to direct them in narrow beams , which can be pointed directly at the receiving antenna.
Microwave Link / Hop
- The connection of two fixed microwave sites via a line of light (LOS) path.
- It is called Hop
Microwave Key Parameters :
- Hertz ( HZ ) :
A measurement of a signal's electromagnetic frequency , expressed as a number of cycles per second.
KHZ : Kilohertz , MHZ : Megahertz , GHZ : Gigahertz , THZ : Terahertz
- Frequency :
The rate of the wave's oscillation , measured in hertz ( HZ )
- Amplitude :
The strength of power level ofthe wave
- Phase :
The particular point in the cycle of a waveform , measured in degrees
- Polarization
The orientation of the electric field driving the wave
Line Of Sight ( LOS )
It is a type of propagation that can transmit and receive data only where transmit and receive stations are in view of each other without any obstacles between them .
Examples are FM radio , Microwave and satellite transmission
Antennas :
Antennas are devices that radiate or receive EM waves of certain frequencies
Microwave Antenna :
An antenna designed to radiate and receive microwave frequencies , therefore is called a microwave antenna .
A metallic physical transmission medium & waves propagate along it .
Microwave energy travels through guided media is called waveguide .
Waveguide Types :
Rectangular Waveguide
Circular waveguide
Elliptical waveguide
Corrugated Waveguide
Involve LOS communication technology.
Affected greatly by environmental constraints including rain fading .
Have very limited penetration capabilities through obstacles such as hills , building and tress .
Signals can be degraded during solar proton events.
Fading :
Loss in signal strength a cross a link caused by atmospheric disturbance link rain or snow that can scatter microwave signals .
The lower frequency microwave bands offer the greatest possible distance - theoretically allowing for links in excess of 50 KM
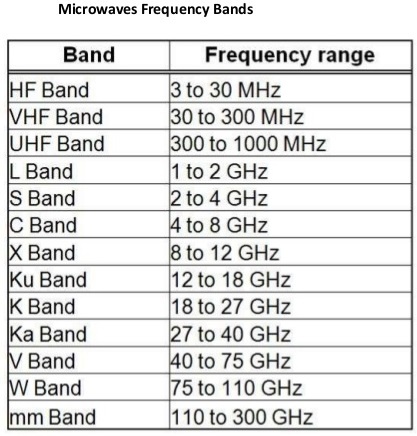
Microwave Frequencies :
Microwave Frequency & it's application
The lower frequency bands offer the greatest possible distance - theoretically allowing for links in excess of 50 KM.
Adaptive Transmit Power Control ( ATPC )
ATPC dynamically adjusts power levels to compensate for any link impediments .
Adaptive Modulation :
Is used dynamically switch modulation schemes according to the prevailing channel conditions .
Typical modulation schemes selected for adaptive modulation are 4QAM , 16QAM , 64QAM , 128QAM , 256QAM , 512QAM and 1024QAM























0 التعليقات:
إرسال تعليق